https://www.bilibili.com/video/av47952931
p46~55
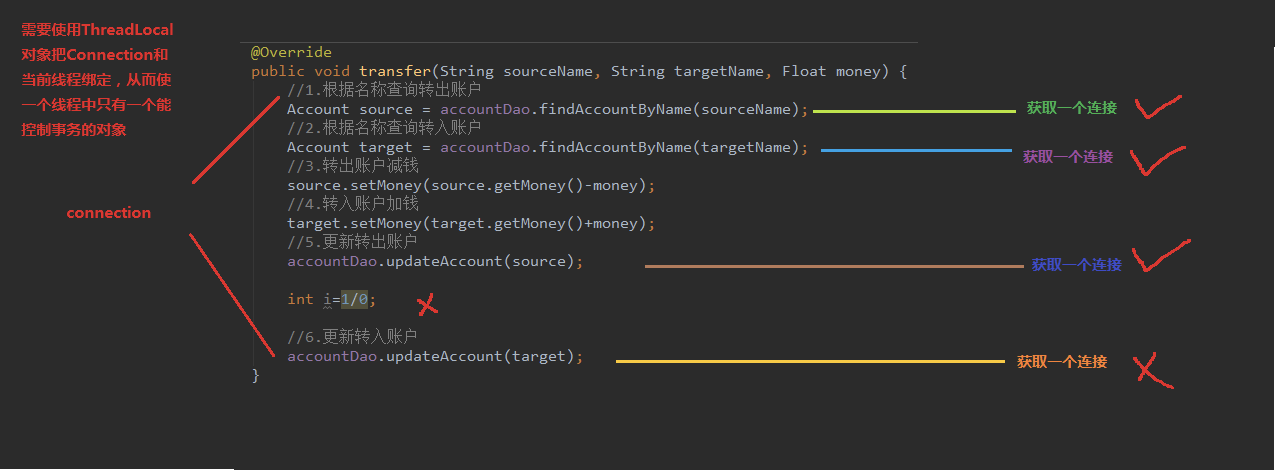
Account案例中转账方法的事务问题

事务控制应该都在业务层,之前的案例中都在持久层,需要修改
写两个工具类
2个工具类
ConnectionUtils
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
|
public class ConnectionUtils {
private ThreadLocal<Connection> tl = new ThreadLocal<Connection>();
private DataSource dataSource;
public void setDataSource(DataSource dataSource) {
this.dataSource = dataSource;
}
public Connection getThreadConnection() {
try{
Connection conn = tl.get();
if (conn == null) {
conn = dataSource.getConnection();
tl.set(conn);
}
return conn;
}catch (Exception e){
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public void removeConnection(){
tl.remove();
}
}
|
TransactionManager
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
|
public class TransactionManager {
private ConnectionUtils connectionUtils;
public void setConnectionUtils(ConnectionUtils connectionUtils) {
this.connectionUtils = connectionUtils;
}
public void beginTransaction(){
try {
connectionUtils.getThreadConnection().setAutoCommit(false);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void commit(){
try {
connectionUtils.getThreadConnection().commit();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void rollback(){
try {
connectionUtils.getThreadConnection().rollback();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void release(){
try {
connectionUtils.getThreadConnection().close();
connectionUtils.removeConnection();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
|
连接还回连接池中后,还需再把连接和线程解绑,否则下次ConnectionUtils中判断是否有连接是true,但这个连接是已经关闭的错误的连接
注入
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| <!-- 配置Connection的工具类 ConnectionUtils -->
<bean id="connectionUtils" class="com.itheima.utils.ConnectionUtils">
<!-- 注入数据源-->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 配置事务管理器-->
<bean id="txManager" class="com.itheima.utils.TransactionManager">
<!-- 注入ConnectionUtils -->
<property name="connectionUtils" ref="connectionUtils"></property>
</bean>
|
代码改造
修改之后不需要在beans.xml中注入dataSource了
1
2
3
4
5
|
<bean id="connectionUtils" class="com.itheima.utils.ConnectionUtils">
</bean>
|
在AccountDaoImpl中加一个ConnectionUtils
1
2
3
4
5
| private ConnectionUtils connectionUtils;
public void setConnectionUtils(ConnectionUtils connectionUtils) {
this.connectionUtils = connectionUtils;
}
|
并且runner获取连接改为
1
| runner.query(connectionUtils.getThreadConnection(),"select * from account",new BeanListHandler<Account>(Account.class));
|
此时,AccountServiceImpl中一个完整的事务流程是
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| public List<Account> findAllAccount() {
try {
txManager.beginTransaction();
List<Account> accounts = accountDao.findAllAccount();
txManager.commit();
return accounts;
}catch (Exception e){
txManager.rollback();
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally {
txManager.release();
}
}
|
但是每个方法都要这样写,很臃肿
而且方法的依赖很严重(如果TransactionManager中beginTransaction方法名改成beginTransaction1,AccountServiceImpl中每一处用到的都要改)
进一步改造:代理
& 现在的依赖有些乱七八糟,在后面Spring的事务控制中解决
动态代理
描述

特点:字节码随用随创建,随用随加载
作用:不修改源码的基础上对方法增强
分类:
用处如:
连接池close方法关闭时不能真正关闭,还要还回池中。可以使用动态代理对其进行增强,把它还回池里
解决中文乱码,request对象的方法增强,用装饰者模式可以实现,也可以用动态代理实现
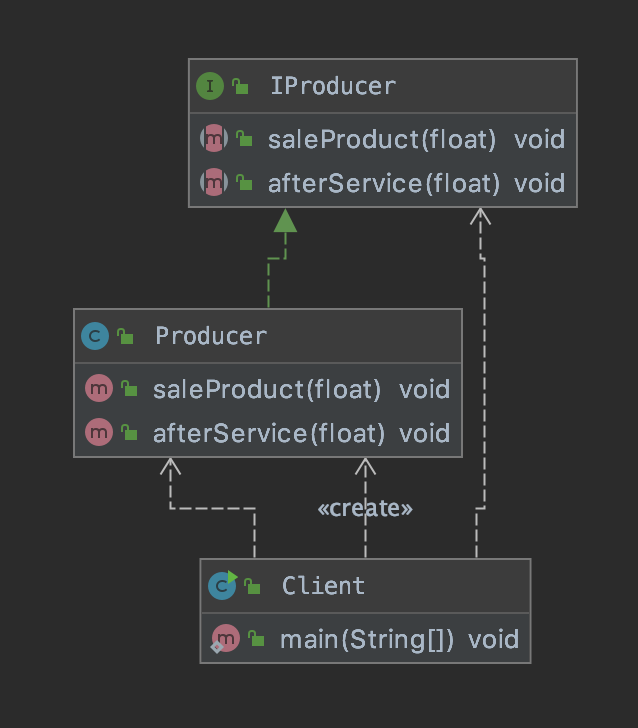
基于接口的动态代理
涉及的类:Proxy
提供者:JDK官方
如何创建代理对象:使用Proxy类中的newProxyInstance方法
创建代理对象的要求:被代理类最少实现一个接口,如果没有则不能使用
newProxyInstance方法的参数:
- ClassLoader:类加载器
它是用于加载代理对象字节码的。和被代理对象使用相同的类加载器。固定写法
- Class[]:字节码数组
它是用于让代理对象和被代理对象有相同方法。固定写法
- InvocationHandler:用于提供增强的代码
写如何代理。一般都是写一个该接口的实现类,通常情况下都是匿名内部类,但不是必须的。此接口的实现类都是谁用谁写
示例

1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
public interface IProducer {
public void saleProduct(float money);
public void afterService(float money);
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
public class Producer implements IProducer{
public void saleProduct(float money){
System.out.println("销售产品,并拿到钱:"+money);
}
public void afterService(float money){
System.out.println("提供售后服务,并拿到钱:"+money);
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
|
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final Producer producer = new Producer();
IProducer proxyProducer = (IProducer) Proxy.newProxyInstance(producer.getClass().getClassLoader(),
producer.getClass().getInterfaces(),
new InvocationHandler() {
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
Object returnValue = null;
Float money = (Float)args[0];
if("saleProduct".equals(method.getName())) {
returnValue = method.invoke(producer, money*0.8f);
}
return returnValue;
}
});
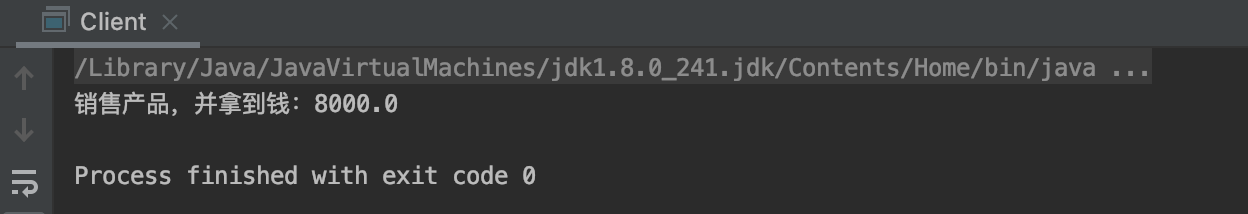
proxyProducer.saleProduct(10000f);
}
}
|

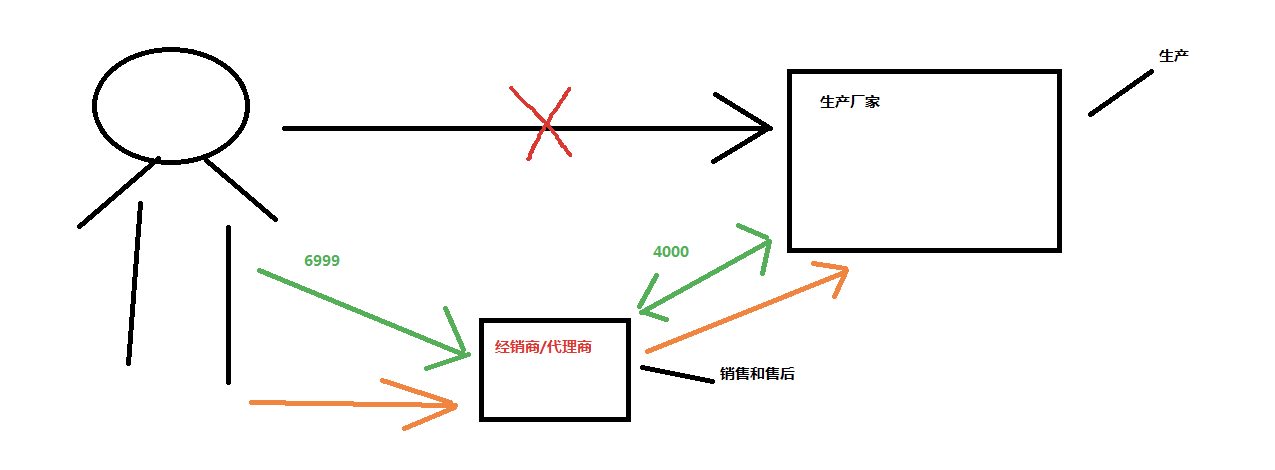
使用代理后,消费者付10000,代理提成20%,生产者拿到8000
并没有对生产者的代码做任何修改,但是实现了增强
此处即为基于接口的动态代理
但是有一个问题
如果生产者没有实现接口,就不能这样用了,会报代理异常
基于子类的动态代理
要求有第三方jar包的支持
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| <dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>cglib</groupId>
<artifactId>cglib</artifactId>
<version>2.1_3</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
|
涉及的类:Enhancer
提供者:第三方cglib库
如何创建代理对象:使用Enhancer类中的create方法
创建代理对象的要求:被代理类不能是最终类
create方法的参数:
- Class:字节码
用于指定被代理对象的字节码
- Callback:用于提供增强的代码
写如何代理。一般是写一个该接口的实现类,通常情况下都是匿名内部类,但不是必须的
此接口的实现类都是谁用谁写
一般写的都是该接口的子接口实现类:MethodInterceptor
示例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
public class Producer {
public void saleProduct(float money){
System.out.println("销售产品,并拿到钱:"+money);
}
public void afterService(float money){
System.out.println("提供售后服务,并拿到钱:"+money);
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
| package com.itheima.cglib;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.Enhancer;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodInterceptor;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodProxy;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final Producer producer = new Producer();
Producer cglibProducer = (Producer)Enhancer.create(producer.getClass(), new MethodInterceptor() {
@Override
public Object intercept(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {
Object returnValue = null;
Float money = (Float)args[0];
if("saleProduct".equals(method.getName())) {
returnValue = method.invoke(producer, money*0.8f);
}
return returnValue;
}
});
cglibProducer.saleProduct(12000f);
}
}
|
使用动态代理实现事务控制
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
|
public class BeanFactory {
private IAccountService accountService;
private TransactionManager txManager;
public final void setAccountService(IAccountService accountService) {
this.accountService = accountService;
}
public void setTxManager(TransactionManager txManager) {
this.txManager = txManager;
}
public IAccountService getAccountService() {
return (IAccountService)Proxy.newProxyInstance(accountService.getClass().getClassLoader(),
accountService.getClass().getInterfaces(),
new InvocationHandler() {
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
if("test".equals(method.getName())){
return method.invoke(accountService,args);
}
Object rtValue = null;
try {
txManager.beginTransaction();
rtValue = method.invoke(accountService, args);
txManager.commit();
return rtValue;
} catch (Exception e) {
txManager.rollback();
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
txManager.release();
}
}
});
}
}
|
并对beans.xml做相应的修改
测试中IAccountService只用Autowird不够了,还需@Qualifier(“proxyAccountService”)
使用动态代理后,消除了重复代码,解除了方法的依赖
但是配置变得繁琐了
更好的方式?——>AOP